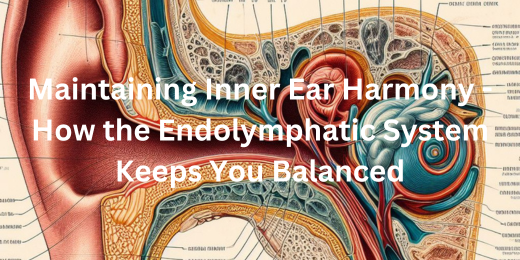
The function of the Endolymphatic System is a crucial aspect of our body’s intricate balance mechanisms. Nestled within the inner ear, this system is responsible for maintaining equilibrium. It consists of a series of canals and sacs filled with a unique fluid called endolymph.
When we move, this fluid shifts, sending signals to our brain about our position in space. This information is then processed to help us stay upright and steady. Additionally, the Endolymphatic System plays a vital role in spatial orientation, allowing us to navigate our surroundings with precision.
It’s a remarkable interplay of biology and physics that ensures we can stand, walk, and move with confidence. Understanding this system sheds light on the intricacies of our body’s design and the remarkable way it enables us to interact with the world around us. Similarly, the circulatory system delivers oxygen, nutrients, and supports organ function.
Anatomy of the Inner Ear and Endolymphatic System
Understanding the function of the Endolymphatic System begins with appreciating its intricate anatomy within the inner ear. This system, a vital component of our auditory and vestibular apparatus, is comprised of several key structures. At its core lies the cochlea, responsible for processing sound vibrations and transmitting them to the brain.
Adjacent to the cochlea are the semicircular canals, which constitute the vestibular system. These canals are filled with endolymph, a specialized fluid that aids in detecting rotational movements of the head. Connected to the canals is the endolymphatic sac, which acts as a reservoir for regulating the volume and pressure of the endolymph.
Together, these components form a finely tuned mechanism that not only facilitates hearing but also maintains our sense of balance and spatial orientation. It’s a testament to the remarkable intricacy of the human body’s design. Likewise, the renal system, consisting of the kidneys and urinary tract, is crucial for filtering waste, maintaining fluid balance, and supporting overall health.
Function of the Endolymphatic System in Balance
The function of the Endolymphatic System is paramount in maintaining our sense of balance. Situated within the inner ear, this intricate system relies on the flow of endolymph, a specialized fluid, to transmit crucial signals to the brain. When we move our head or change position, this fluid shifts, sending precise information about our spatial orientation.
The brain then processes these signals, allowing us to stand upright, walk steadily, and even navigate complex terrains. Moreover, the Endolymphatic System plays a pivotal role in detecting rotational movements, ensuring that we can turn our heads and change direction smoothly.
It’s a testament to the finely-tuned biological engineering that enables us to interact seamlessly with our environment. Understanding this system sheds light on the profound intricacies that govern our everyday movements and actions.
Disorders Affecting the Endolymphatic System
Understanding the function of the Endolymphatic System is imperative in comprehending the various disorders that can affect this crucial sensory mechanism. One of the common disorders is Meniere’s Disease, characterised by a buildup of excess endolymph fluid. This can lead to symptoms like vertigo, hearing loss, and a sensation of fullness in the ear.
Another condition is Endolymphatic Hydrops, which shares similarities with Meniere’s but may not always involve vertigo. Additionally, benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) can disrupt the normal flow of endolymph due to displaced calcium crystals, leading to sudden bouts of vertigo.
The vestibular system maintains balance and spatial awareness in the human body. Vestibular Migraines, while primarily a neurological condition, can also impact the endolymphatic system, causing episodes of severe dizziness. These disorders underscore the vital role played by the Endolymphatic System in our overall balance and equilibrium, and the significant impact that its dysfunction can have on our daily lives.
Tips for Maintaining Inner Ear Harmony
Maintaining the function of the Endolymphatic System is crucial for overall balance and well-being. To ensure inner ear harmony, consider a few simple yet effective tips. Firstly, stay hydrated. Proper hydration supports the optimal flow of endolymph fluid, aiding in its vital role of transmitting signals to the brain.
Additionally, regular exercise promotes good circulation, benefiting the inner ear’s health. Avoiding loud noises and using ear protection in noisy environments safeguards delicate structures in the inner ear. A balanced diet rich in nutrients like magnesium and vitamins B and C can contribute to the system’s resilience.
Lastly, managing stress through techniques like meditation or deep breathing exercises can indirectly benefit the Endolymphatic System, as stress can exacerbate certain inner ear conditions. These tips, when incorporated into a daily routine, play a significant role in maintaining the delicate balance of the inner ear and the function of the Endolymphatic System
Conclusion: Importance of Caring for the Endolymphatic System for Balance and Well-being
In conclusion, appreciating the function of the Endolymphatic System is paramount for maintaining balance and overall well-being. This intricate system, nestled within the inner ear, plays a pivotal role in ensuring we can stand steady, walk confidently, and navigate our surroundings effortlessly.
Disorders affecting this system can have profound impacts on daily life, underscoring the importance of its care. Simple practices like staying hydrated, exercising regularly, and protecting our ears from excessive noise can go a long way in supporting the Endolymphatic System.
A balanced diet and stress management techniques further contribute to its optimal function. By nurturing this delicate mechanism, we not only safeguard our physical equilibrium but also enhance our quality of life. It’s a testament to the interconnectedness of our body’s systems, and the profound impact that even the most intricate components can have on our overall well-being.