Symptoms of diabetes
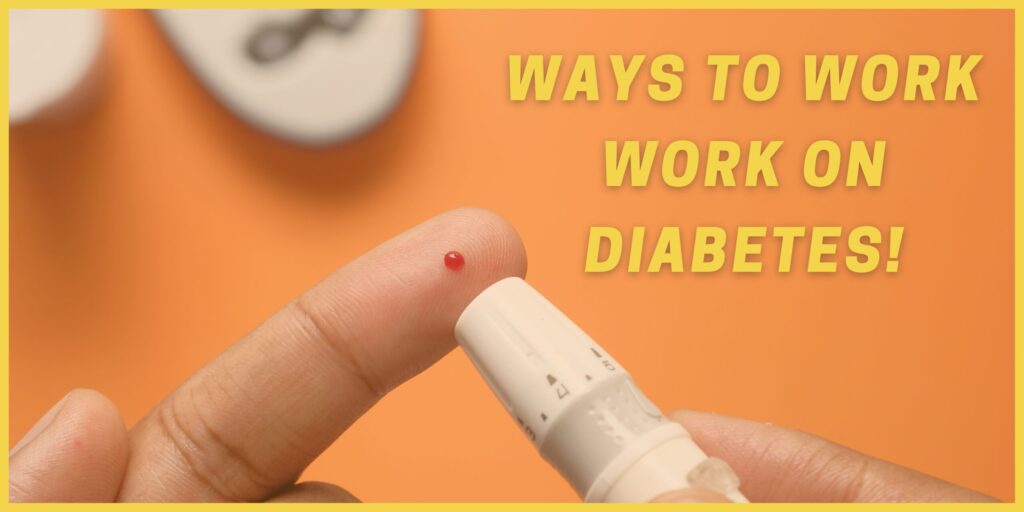
The symptoms of diabetes, along with causes, treatment, and prevention, are explained in great depth. Diabetes is a persistent disease that develops when the pancreas stops producing insulin or when the body’s insulin isn’t properly utilised. Pancreatic insulin is a hormone that acts as a gatekeeper to allow glucose from our diet to enter the cells of our body for energy production. In the blood, all carbohydrate products are converted into glucose. Insulin aids glucose absorption into cells. Hyperglycemia is a condition in which the body cannot make or utilise insulin properly, resulting in elevated glucose levels in the blood. When you have diabetes, your system does not produce enough insulin or does not use it as well as it should. When there is insufficient insulin or cells cease reacting to insulin, an abnormal amount of blood sugar remains in the bloodstream. Over time, this can result in major health concerns, including heart disease, eyesight loss, and renal illness. Type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes are the three main kinds of diabetes.
Symptoms of diabetes
Nausea, vomiting, and stomach cramps are common symptoms of type 1 diabetes. It is possible for type 1 diabetes symptoms to appear in as little as a few weeks or months, and they can be exceedingly severe in certain cases. Type 1 diabetes typically manifests itself during childhood, adolescence, or early adulthood, but it can occur at any age. Symptoms of type 2 diabetes can take years to appear. Some folks are completely oblivious to any signs. Although type 2 diabetes typically affects adults, adolescents and teenagers are becoming more and more affected. Because symptoms might be difficult to detect, knowing the potential risks for type 2 diabetes is crucial. If you are experiencing any of the symptoms indicated above, you should make an appointment with your doctor as soon as possible to receive treatment. The symptoms of diabetes include experiencing hazy eyesight, numb or tingling hands or feet, being extremely weary, having extremely dry skin, sores that take a long time to cure, and having more infections than usual. Gestational diabetes, or diabetes that develops during pregnancy, normally has no symptoms. If you’re expecting a child, your physician should examine you for gestational diabetes between weeks 24 and 28. If necessary, you can make modifications to safeguard your health and your baby’s health.
Causes of diabetes
Each form of diabetes has its own set of causes, which are distinct. Frequent urination, particularly at night, and extreme thirst are some common symptoms of diabetes. In patients with type 1 diabetes, doctors are unsure about the specific causation of type 1 diabetes. The immune system targets and damages insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas for unknown reasons. Genes might have a role in the development of some persons. Additionally, it is possible that a virus triggers an immune system attack. Diabetes type 2 is caused by a mix of hereditary and lifestyle factors. Obesity or being overweight also raises your risk. Carrying excess weight, particularly in the abdomen, causes your cells to be more resilient to insulin’s influence on your blood sugar. This disorder is hereditary, and family members inherit genes that increase their risk of developing type 2 diabetes and obesity. Because of hormonal changes that take place during pregnancy, pregnant women can develop gestational diabetes. The placenta generates hormones that reduce the sensitivity of a pregnant woman’s cells to the actions of insulin, and pregnancy-related high blood sugar can occur from this. Women who are heavy or acquire excessive weight during pregnancy are more prone to develop gestational diabetes. Both genetic and environmental variables play vital roles in the development of diabetes.
Treatment and Prevention
Diabetes is managed by physicians using a variety of drugs. Some of these medications are given orally, while others are administered via injection. Losing weight without exerting effort and feeling extremely hungry are the symptoms of diabetes. Insulin is the primary medication used to treat type 1 diabetes, and it acts as a substitute for the hormone that your body is unable to manufacture. Certain individuals can control type 2 diabetes by diet and exercise. If lifestyle changes alone are insufficient to control your blood sugar, medication will be required. You’ll have to examine your blood sugar many times a day throughout pregnancy. If it is elevated, dietary adjustments and exercise may or may not be sufficient to reduce it. Your doctor will prescribe a medicine or mix of medications depending on the kind of diabetes you possess — and its reason. Type 1 diabetes is incurable since it is caused by an immune system malfunction. Certain factors that contribute to type 2 diabetes, including your genes or age, are also beyond your control. Numerous additional risk factors for diabetes, on the other hand, are manageable. The majority of diabetes prevention strategies entail making small changes to your diet and exercise routine. If you have been tested with prediabetes, the following steps can help you delay or avoid developing type 2 diabetes: If you are overweight or obese, make an effort to lose weight. Participate in at least 150 minutes of aerobic exercise every week, such as walking or cycling. Eliminate saturated and trans fats from your diet, as well as refined carbs. Consume a greater variety of fruits, veggies, and whole grains. Uyir organic farmers market provides people with the highest quality organic fruits and vegetables for a healthy lifestyle.